Optimizing Livestock: Precision Farming Tech for Feeding & Health

Precision Livestock Farming (PLF) utilizes technology to monitor and manage livestock, optimizing feeding strategies and health management for improved efficiency and sustainability in agriculture.
In today’s agriculture, efficiency and sustainability are key. Precision Livestock Farming: Using Technology to Optimize Feeding and Health is revolutionizing how farmers manage their animals, leading to healthier livestock, reduced waste, and increased profits. Let’s dive into this cutting-edge approach.
What is Precision Livestock Farming?
Precision Livestock Farming (PLF) involves using various technologies to monitor and manage livestock in real-time. This data-driven approach allows farmers to make informed decisions about feeding, health, and overall animal welfare.
By implementing PLF techniques, farmers can identify and address issues early, leading to more efficient and sustainable farming practices.
Key Technologies in PLF
PLF incorporates a range of technologies to monitor and manage livestock effectively. Here are some essential components:
- Sensors: These devices track various parameters, such as an animal’s body temperature, activity levels, and feeding behavior.
- Data Analytics: The data collected by sensors is analyzed to identify trends and anomalies, providing insights into animal health and performance.
- Automated Systems: Automated feeding and watering systems ensure that animals receive the right amount of resources at the right time.
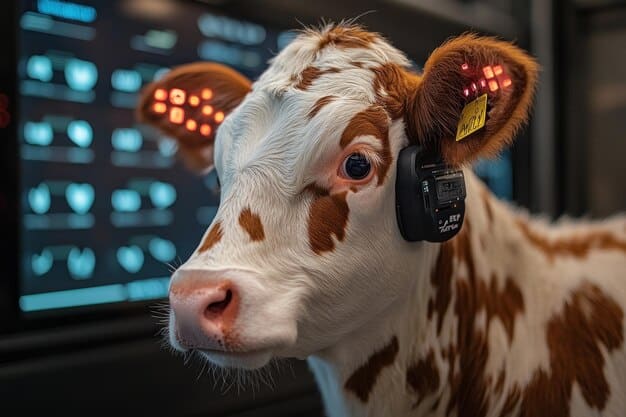

Essentially, PLF is about using technology to gain a deeper understanding of each animal’s needs, allowing for personalized care and management.
Enhancing Feeding Strategies with PLF
One of the most significant benefits of Precision Livestock Farming is its ability to improve feeding strategies. Traditional methods often involve providing the same feed to all animals, which can lead to inefficiencies and waste.
PLF enables farmers to tailor feeding plans to meet the specific needs of each animal, optimizing nutrient intake and reducing feed costs.
Individualized Feeding
PLF systems can monitor individual animal feeding behaviors and adjust feed rations accordingly. This ensures that each animal receives the nutrients it needs to thrive.
For example, sensors can track how much each cow eats and drinks, allowing farmers to identify animals that may not be getting enough nutrients.
Reducing Feed Waste
By monitoring feed consumption in real-time, PLF systems can help reduce waste. Farmers can adjust feed delivery to match the animals’ actual needs, preventing excess feed from being discarded.
This not only saves money but also reduces the environmental impact of farming by minimizing the resources needed to produce feed.
In short, PLF ensures that livestock receive the precise nutrition they require, minimizing waste and maximizing overall efficiency.
Improving Animal Health Through Technology
Animal health is a critical aspect of livestock farming. Precision Livestock Farming offers several ways to monitor and improve the health of animals, reducing the need for antibiotics and other medications.
By detecting health issues early, farmers can provide timely treatment and prevent the spread of disease.

Early Disease Detection
PLF systems can monitor various health indicators, such as body temperature, heart rate, and activity levels. Any deviations from normal patterns can signal an early warning of disease.
For example, sensors can detect a slight increase in a cow’s body temperature, indicating a potential infection. This allows farmers to isolate the animal and provide treatment before the condition worsens.
Reducing Antibiotic Use
By detecting and addressing health issues early, PLF can help reduce the need for antibiotics. Farmers can focus on preventative measures and targeted treatments, minimizing the risk of antibiotic resistance.
- Monitoring Vital Signs: Continuous monitoring helps detect subtle changes that may indicate illness.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Farmers can make informed decisions about treatment based on real-time data.
- Improved Animal Welfare: Early detection and treatment improve the overall well-being of the animals.
Ultimately, PLF leads to healthier livestock and promotes more sustainable farming practices.
The Role of Data Analytics in PLF
Data analytics is at the heart of Precision Livestock Farming. The data collected by sensors and other technologies is analyzed to provide insights into animal health, feeding behavior, and overall farm performance.
These insights enable farmers to make informed decisions and optimize their operations.
Analyzing Animal Behavior
Data analytics can reveal patterns in animal behavior that would be difficult to detect manually. For example, changes in activity levels or feeding patterns can indicate stress or illness.
By analyzing this data, farmers can identify potential issues early and take corrective action.
Optimizing Farm Management
Data analytics can also be used to optimize farm management practices. For example, farmers can use data to determine the most efficient feeding schedules or to identify areas where they can reduce waste.
- Farm Performance: Analyze data to identify inefficiencies and improve overall productivity.
- Predictive Analytics: Use data to forecast future trends and make proactive decisions.
- Decision Support: Provide farmers with the information they need to make informed choices.
Data analytics is a powerful tool that can help farmers improve the efficiency and sustainability of their operations.
Challenges and Opportunities in Implementing PLF
While Precision Livestock Farming offers many benefits, there are also challenges to consider. Implementing PLF requires an investment in technology and training, and it may take time for farmers to see a return on their investment.
However, the long-term benefits of PLF make it a worthwhile investment for many farmers.
Initial Investment Costs
The initial cost of implementing PLF can be a barrier for some farmers. Sensors, data analytics software, and automated systems can be expensive. However, government subsidies and other financial incentives may be available to help offset these costs.
Additionally, the long-term savings from reduced feed waste, improved animal health, and increased productivity can outweigh the initial investment.
Training and Expertise
Implementing PLF requires farmers to develop new skills and expertise. They need to be able to interpret data, use technology, and make informed decisions based on the information they receive.
Training programs and educational resources can help farmers develop the skills they need to succeed with PLF.
Despite the challenges, PLF presents many opportunities for farmers who are willing to embrace new technologies and approaches.
The Future of Precision Livestock Farming
The future of Precision Livestock Farming is bright. As technology continues to advance, PLF systems will become more sophisticated and affordable, making them accessible to a wider range of farmers.
PLF has the potential to transform the livestock industry, making it more efficient, sustainable, and humane.
Advancements in Technology
Future PLF systems will likely incorporate more advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies can analyze data in real-time and provide even more detailed insights into animal health and behavior.
- AI-Powered Analytics: Use AI to identify complex patterns and predict future trends.
- Robotics: Implement robotic systems for tasks such as feeding and cleaning.
- Connectivity: Improve connectivity between sensors and data analytics platforms.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations
As consumers become more concerned about sustainability and animal welfare, PLF will play an increasingly important role. PLF can help farmers reduce their environmental impact and improve the lives of their animals.
This includes reducing greenhouse gas emissions, minimizing waste, and ensuring that animals receive the best possible care.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 📊 Data-Driven Insights | Utilizing real-time data for informed decision-making in livestock management. |
| 🍎 Optimized Feeding | Tailoring feed to individual animal needs, reducing waste and improving nutrition. |
| ⚕️ Enhanced Health Monitoring | Early detection of health issues, reducing antibiotic use and improving welfare. |
| 🌱 Sustainable Farming | Minimizing environmental impact through efficient resource use and waste reduction. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
The primary goal is to optimize animal health, feeding, and overall welfare through the use of data-driven technologies, leading to more efficient and sustainable farming practices.
▼
PLF systems monitor individual animal feeding behaviors, allowing farmers to tailor feed rations and prevent overfeeding, thereby minimizing feed waste and reducing costs.
▼
Common technologies include sensors to monitor vital signs and behavior, data analytics software to interpret data, and automated systems for feeding and watering livestock.
▼
By detecting health issues early and enabling targeted treatments, PLF helps reduce the need for broad-spectrum antibiotics, contributing to efforts to combat antibiotic resistance.
▼
The main challenges include the initial investment costs, the need for specialized training, and ensuring that the collected data is properly analyzed and acted upon by the farm management.
Conclusion
Precision Livestock Farming: Using Technology to Optimize Feeding and Health is transforming the agriculture industry, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve animal welfare, reduce waste, and increase efficiency. By embracing these innovative technologies, farmers can create more sustainable and profitable operations, ensuring a brighter future for livestock farming.