Agroforestry in the US: Integrating Trees for Farm Sustainability and Profit
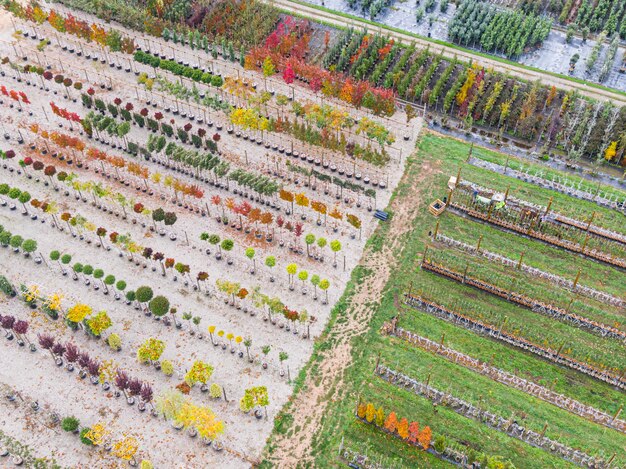

Agroforestry in the US involves strategically integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural lands to enhance biodiversity, improve soil health, and create diversified income streams for farmers, promoting long-term ecological and economic sustainability.
Discover how integrating trees into farms through agroforestry in the US: How to Integrate Trees into Farms for Long-Term Sustainability and Profitability can revolutionize sustainable agriculture, offering ecological benefits and improved financial outcomes for American farmers.
What is Agroforestry and Why is it Important?
Agroforestry represents a holistic approach to land management that intentionally combines agriculture and forestry. This integrated system can enhance farm productivity, ecological health, and economic resilience.
In the US, agroforestry practices are gaining traction as farmers seek more sustainable and profitable farming methods. By strategically incorporating trees into agricultural landscapes, agroforestry systems offer a multitude of benefits, from improved soil fertility and water management to enhanced biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
Key Principles of Agroforestry
Agroforestry is built on several core principles that guide its implementation:
- Integration: Combining trees and crops or livestock in a way that optimizes interactions and benefits.
- Diversity: Utilizing a variety of tree species and agricultural products to enhance resilience and market opportunities.
- Sustainability: Designing systems that promote long-term ecological and economic health.
Benefits of Agroforestry
Agroforestry offers a wide array of benefits that extend beyond conventional farming practices:
- Soil Health: Trees improve soil structure, reduce erosion, and enhance nutrient cycling.
- Water Management: Agroforestry systems can increase water infiltration, reduce runoff, and improve water quality.
- Biodiversity: Integrating trees into farms provides habitat for wildlife and supports a diverse ecosystem.
- Carbon Sequestration: Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to mitigate climate change.

In conclusion, agroforestry is a sustainable and advantageous agricultural practice that integrates trees into farming systems. Its importance lies in its ability to enhance ecological balance, improve long-term profitability, and promote resilience in agricultural landscapes.
Types of Agroforestry Practices in the US
Agroforestry encompasses a variety of practices, each tailored to specific environmental conditions and farming goals. Understanding these different types can help farmers choose the best approach for their land and objectives.
Several agroforestry systems are commonly used in the US, including alley cropping, silvopasture, forest farming, windbreaks, and riparian buffers. Each of these practices offers unique benefits and can be adapted to various agricultural settings.
Alley Cropping
Alley cropping involves planting rows of trees or shrubs with wide alleys in between, where crops are grown. This system can improve soil fertility, reduce erosion, and provide additional income from tree products.
Silvopasture
Silvopasture combines trees, forage, and livestock in an integrated system. Trees provide shade and shelter for animals, while livestock help manage vegetation and fertilize the soil. This practice can enhance animal health, improve forage production, and create diversified income streams.
Forest Farming
Forest farming involves growing high-value specialty crops under the canopy of a forest. This practice can generate income from non-timber forest products, such as mushrooms, herbs, and medicinal plants, while conserving forest ecosystems.
Windbreaks
Windbreaks are rows of trees or shrubs planted to protect crops and livestock from wind. These barriers can reduce soil erosion, improve crop yields, and provide habitat for wildlife.
Riparian Buffers
Riparian buffers are vegetated areas along waterways that help filter pollutants, stabilize stream banks, and provide habitat for aquatic life. These buffers can improve water quality, reduce erosion, and enhance biodiversity.
- Water Quality: Buffers filter pollutants and excess nutrients from runoff.
- Erosion Control: Vegetation stabilizes stream banks and reduces soil erosion.
- Habitat Provision: Riparian buffers provide habitat for fish, amphibians, and other aquatic species.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of agroforestry practices is crucial for farmers looking to integrate trees into their operations. By selecting the appropriate system, farmers can maximize the ecological and economic benefits of agroforestry.
Implementing Agroforestry: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing agroforestry involves careful planning and execution to ensure its success. Following a step-by-step guide can help farmers navigate the process and achieve their desired outcomes.
The initial steps involve assessing your farm’s resources and goals, selecting appropriate tree species and agricultural practices, and designing a system that fits your specific needs. Proper site preparation, planting techniques, and ongoing management are essential for the long-term success of your agroforestry system.
Here are key steps in implementing agroforestry:
- Assess Your Farm: Evaluate your soil, climate, water resources, and existing vegetation.
- Define Your Goals: Determine what you want to achieve with agroforestry, such as improved soil health, increased income, or enhanced biodiversity.
- Select Tree Species: Choose trees that are well-suited to your environment and meet your specific needs.
Detailed Planning Considerations
Careful planning is essential for determining the layout and management strategies.
- Layout Design: Consider the spacing and arrangement of trees and crops to optimize sunlight, water, and nutrient availability.
- Management Strategies: Develop a plan for pruning, irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
- Financial Planning: Evaluate the costs and potential returns of your agroforestry system to ensure its economic viability.
Site Preparation and Planting
Proper ground preparation and planting techniques are crucial for the success.
- Site Preparation: Prepare the soil by removing weeds, rocks, and debris.
- Planting Techniques: Use appropriate planting methods to ensure the trees establish well.
- Protecting Seedlings: Protect young trees from animal browse and weed competition.
In conclusion, successful implementation of agroforestry requires careful planning, preparation, and ongoing management. By following a step-by-step guide, farmers can increase the likelihood of achieving their goals and realizing the full benefits of agroforestry.
Economic Benefits of Agroforestry for US Farmers
Agroforestry offers a range of economic benefits that can enhance the profitability and resilience of US farms. Diversifying income streams, reducing input costs, and increasing land value are key economic advantages.
By incorporating trees into their operations, farmers can generate income from timber, fruits, nuts, and other tree products. Agroforestry systems can also reduce the need for fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation, resulting in lower input costs. Additionally, agroforestry can increase the value of farmland by improving its ecological health and aesthetic appeal.
- Multiple Income Streams: Harvest timber, fruits, nuts, or specialty forest products.
- Reduced Costs: Decrease the need for fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation.
- Increased Land Value: Enhance the ecological health and aesthetic appeal of farmland.
Specific Economic Advantages
Agroforestry provides a multitude of ways to strengthen a farm’s financial situation.
Direct revenues from tree products.
Savings on inputs due to improved soil and natural pest control.
Creating valuable ecosystem services like carbon storage.
In conclusion, agroforestry provides substantial economic benefits for farmers, from diversified income streams to reduction in input costs. These advantages can transform a farm into more successful business.
Overcoming Challenges in Agroforestry
While agroforestry offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges that farmers need to address. These challenges may include initial investment costs, lack of technical knowledge, and regulatory hurdles.
To overcome these challenges, farmers can seek financial assistance through grants and loans, participate in training programs and workshops, and work with government agencies to navigate regulations. By addressing these challenges proactively, farmers can increase the likelihood of success with agroforestry.
- Initial Investment Costs: Trees and systems require a large upfront investment.
- Lack of Knowledge: Effective agroforestry requires a deep technical knowledge and experience.
- Regulatory Hurdles: There could be a number of required permits and permissions.
Strategies for Success
Farmers can take key steps to lessen the problems, the most important factors are:
Seeking financial from government and non-government facilities.
Participating in different training programmes.
In conclusion, while agroforestry presents its challenges, farmers can use key strategies to navigate them. As they do, the chances of a successful and mutually beneficial ecosystem grow substantially.
Government Programs and Support for Agroforestry in the US
Several government programs and initiatives support agroforestry in the US, providing technical assistance, financial incentives, and educational resources to farmers.
These programs are designed to encourage the adoption of agroforestry practices and promote sustainable land management. The USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS), the Farm Service Agency (FSA), and the US Forest Service (USFS) offer various programs that can help farmers implement and manage agroforestry systems.
USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS)
The NRCS provides technical and financial assistance to farmers through programs such as the Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP) and the Conservation Stewardship Program (CSP). These programs offer payments and support for implementing agroforestry practices.
Farm Service Agency (FSA)
The FSA provides farm loans and disaster assistance to farmers. These programs can help farmers finance the implementation of agroforestry systems and recover from natural disasters that may impact their operations.
US Forest Service (USFS)
The USFS conducts research, provides technical assistance, and manages national forests and grasslands. The agency works with farmers and landowners to promote sustainable forestry practices, including agroforestry.
In conclusion, for farmers interested in incorporating agroforestry into their management systems can find support from a number of government programmes. Those programmes have provided support, education, tools and help and make it simpler to implement and ensure that agroforestry is sustainable.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🌳 Agroforestry Definition | Integration of trees with crops or livestock for sustainability. |
| 🌱 Soil Benefits | Improved soil structure, reduced erosion, enhanced nutrients. |
| 💰 Economic Gains | Diversified income, reduced costs, increased land value. |
| 🤝 Government Support | Programs like NRCS and FSA offer financial and technical aid. |
FAQ
The primary goal of agroforestry is to integrate trees and shrubs into agricultural systems to enhance ecological benefits and economic productivity, creating a sustainable land management approach.
Agroforestry improves soil health by increasing organic matter, improving soil structure, reducing erosion, and enhancing nutrient cycling through the decomposition of leaf litter and root biomass.
Common agroforestry practices in the US include alley cropping (planting crops between rows of trees), silvopasture (integrating trees, forage, and livestock), and windbreaks (planting trees to protect crops from wind).
Agroforestry boosts profitability by diversifying income through timber, fruits, and nuts, reducing input costs by improving soil fertility, and enhancing land value with improved ecological health.
Government support for agroforestry is available through USDA programs like the Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP) and the Conservation Stewardship Program (CSP), offering technical and financial assistance.
Conclusion
Agroforestry in the US: How to Integrate Trees into Farms for Long-Term Sustainability and Profitability offers a transformative approach to land management, promoting sustainable agriculture through the integration of trees. By adopting agroforestry practices, farmers can enhance biodiversity, improve soil health, and create diversified income streams, ultimately contributing to a more resilient and profitable agricultural sector.





