US Vertical Farming Market: Tech Trends and Growth Drivers

US Vertical Farming Market: Which Technologies Are Gaining Traction and Why? reveals that LED lighting, hydroponics, and AI-driven automation are significantly reshaping urban agriculture, enhancing crop yields, and promoting sustainable food production practices across the United States.
The US Vertical Farming Market: Which Technologies Are Gaining Traction and Why? is rapidly evolving, driven by the demand for locally sourced, sustainable produce and advancements in agricultural technology. As urban populations grow, vertical farming offers a solution to reduce transportation costs, minimize environmental impact, and ensure year-round crop production. Let’s delve into the key technologies powering this agricultural revolution.
Understanding the US Vertical Farming Market
The US vertical farming market represents a significant shift in agricultural practices by optimizing space usage and resource efficiency. This approach is becoming increasingly crucial as traditional farming faces challenges from climate change, water scarcity, and land degradation. By understanding the market dynamics, we can better appreciate the technological advancements driving its growth.
Market Size and Growth
The vertical farming market in the US has seen substantial growth in recent years, with projections indicating continued expansion. This growth is fueled by increasing investments, technological innovations, and consumer demand for locally grown, pesticide-free produce. The integration of advanced technologies is enabling vertical farms to achieve higher yields and better quality crops.
Key Drivers and Challenges
Several factors drive the growth of vertical farming in the US. These include the need for sustainable agriculture, the desire to reduce food miles, and the ability to produce crops year-round in controlled environments. However, the market also faces challenges such as high initial investment costs, energy consumption, and the need for skilled labor to manage complex systems.
- Demand for Local Produce: Consumers are increasingly seeking locally sourced food to support local economies and reduce their environmental footprint.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in LED lighting, hydroponics, and automation are making vertical farming more efficient and cost-effective.
- Environmental Concerns: Vertical farming reduces water usage, eliminates the need for pesticides, and minimizes land use, addressing key environmental challenges.
In conclusion, understanding the US vertical farming market involves recognizing its growth drivers, challenges, and the crucial role technology plays in overcoming obstacles and optimizing operations.
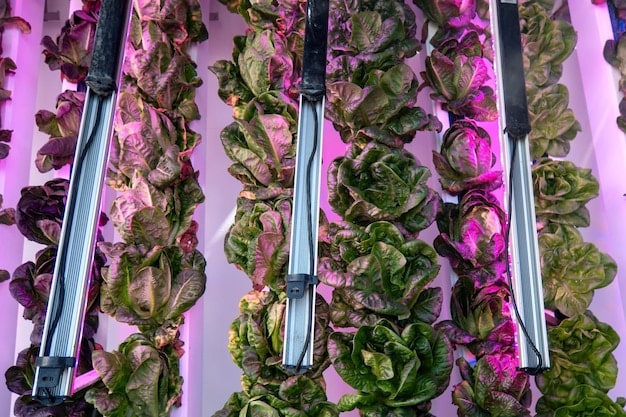

LED Lighting’s Role in Optimizing Crop Growth
LED lighting has emerged as a pivotal technology in vertical farming, offering numerous advantages over traditional lighting systems. By providing tailored light spectrums and reducing energy consumption, LEDs are optimizing crop growth and enhancing the efficiency of vertical farms across the US.
Benefits of LED Lighting
LEDs offer several benefits for vertical farming, including energy efficiency, customizable light spectrums, and reduced heat emission. These advantages contribute to lower operating costs, improved crop quality, and the ability to grow a wider range of crops.
Research and Development
Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on optimizing LED light spectrums for specific crops. Studies have shown that different wavelengths of light can influence plant growth, development, and nutritional content. This research is enabling vertical farms to fine-tune their lighting systems for maximum efficiency and yield.
- Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume significantly less energy than traditional lighting systems, reducing operating costs.
- Customizable Spectrums: LEDs can be tuned to provide specific wavelengths of light that promote optimal plant growth.
- Reduced Heat Emission: LEDs produce less heat, minimizing the need for cooling systems and further reducing energy consumption.
In summary, LED lighting is a crucial technology in vertical farming, offering significant benefits for energy efficiency, crop optimization, and overall sustainability. Continued research and development will further enhance the role of LEDs in shaping the future of agriculture.
Hydroponics: A Water-Efficient Cultivation Method
Hydroponics is a soilless cultivation method that plays a vital role in vertical farming by conserving water and maximizing nutrient delivery. This technology allows plants to grow in nutrient-rich water solutions, eliminating the need for soil and reducing water consumption by up to 90% compared to traditional farming.
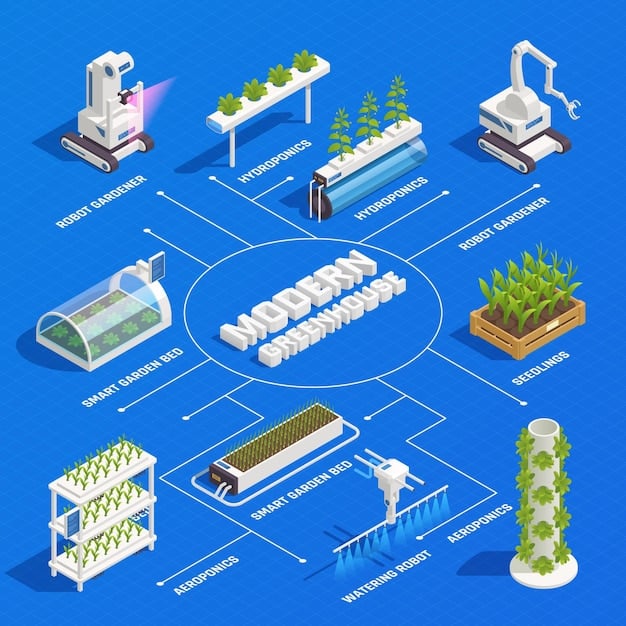
Types of Hydroponic Systems
Various types of hydroponic systems are used in vertical farming, each with its own advantages and applications. These include deep water culture (DWC), nutrient film technique (NFT), and aeroponics. Understanding the different systems is essential for choosing the most suitable method for specific crops and environments.
Water and Nutrient Management
Effective water and nutrient management is crucial for successful hydroponic cultivation. Vertical farms use automated systems to monitor and adjust nutrient levels, pH, and water quality, ensuring optimal growing conditions for plants. These systems help to prevent nutrient deficiencies, diseases, and other issues that can impact crop yield and quality.
- Deep Water Culture (DWC): Plants are suspended in nutrient-rich water, allowing their roots to absorb essential elements.
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): Plants grow in shallow channels with a continuous flow of nutrient solution over their roots.
- Aeroponics: Plants are suspended in the air, and their roots are periodically sprayed with nutrient solution.
In conclusion, hydroponics is a key technology in vertical farming, offering significant advantages in water conservation, nutrient delivery, and overall resource efficiency. The choice of hydroponic system and effective water and nutrient management are critical for achieving optimal crop yields and quality.
AI and Automation in Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are transforming vertical farming by enhancing operational efficiency and reducing labor costs. These technologies enable vertical farms to monitor and control environmental parameters, automate planting and harvesting processes, and optimize resource utilization.
Environmental Control Systems
AI-powered environmental control systems are used to monitor and adjust temperature, humidity, CO2 levels, and other environmental parameters in vertical farms. These systems use sensors and algorithms to maintain optimal growing conditions for plants, ensuring consistent crop quality and yield.
Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation are used in various aspects of vertical farming, including planting, harvesting, and packaging. These technologies reduce the need for manual labor, improve efficiency, and minimize the risk of human error. Automated systems can also collect data on plant growth and health, providing valuable insights for optimizing operations.
- Automated Planting: Robotic systems can precisely plant seeds or seedlings at optimal spacing and depth.
- Automated Harvesting: Robots can identify and harvest ripe crops, reducing labor costs and minimizing damage.
- Data Collection and Analysis: AI algorithms analyze data collected from sensors and cameras to identify trends and optimize growing strategies.
In summary, AI and automation are critical technologies for enhancing operational efficiency, reducing labor costs, and improving crop quality in vertical farming. These advancements are making vertical farms more competitive and sustainable.
The Role of Data Analytics in Improving Crop Yields
Data analytics is playing an increasingly important role in vertical farming by providing insights into plant growth, health, and environmental conditions. By analyzing data collected from sensors, cameras, and other sources, vertical farms can optimize their growing strategies and improve crop yields.
Data Collection and Analysis
Vertical farms collect vast amounts of data on various parameters, including temperature, humidity, light levels, nutrient levels, and plant growth rates. This data is analyzed using statistical models and machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and trends that can inform decision-making.
Predictive Modeling
Predictive modeling techniques are used to forecast crop yields and identify potential problems before they occur. By analyzing historical data and current conditions, predictive models can help vertical farms optimize their growing strategies and minimize the risk of crop failures.
- Optimizing Environmental Parameters: Data analytics can identify the optimal temperature, humidity, and light levels for specific crops.
- Predicting Crop Yields: Predictive models can forecast crop yields based on historical data and current conditions.
- Identifying Potential Problems: Data analytics can identify early signs of plant stress, disease, or nutrient deficiencies.
In conclusion, data analytics is a powerful tool for improving crop yields and optimizing operations in vertical farming. By collecting and analyzing data on various parameters, vertical farms can make informed decisions and ensure consistent crop quality and yield.
Economic and Environmental Impact of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming has the potential to generate significant economic and environmental benefits by reducing transportation costs, conserving water, and minimizing land use. As the technology advances and becomes more widely adopted, the positive impacts will become even more pronounced.
Economic Benefits
The economic benefits of vertical farming include reduced transportation costs, lower labor costs, and increased crop yields. By producing crops locally, vertical farms can reduce the need for long-distance transportation, lowering costs and reducing carbon emissions. Automation and AI can further reduce labor costs, and optimized growing conditions can increase crop yields.
Environmental Benefits
The environmental benefits of vertical farming include reduced water usage, minimized land use, and the elimination of pesticides and herbicides. Vertical farms use up to 90% less water than traditional farms, and they can be located in urban areas, reducing the need for agricultural land. The controlled environment of vertical farms also eliminates the need for pesticides and herbicides, promoting sustainable agriculture.
- Reduced Transportation Costs: Producing crops locally reduces the need for long-distance transportation.
- Conserved Water: Vertical farms use up to 90% less water than traditional farms.
- Minimized Land Use: Vertical farms can be located in urban areas, reducing the need for agricultural land.
In summary, vertical farming offers significant economic and environmental benefits, making it a sustainable and viable solution for meeting the growing demand for food. As the technology continues to evolve, the positive impacts will become even more pronounced, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient food system.
| Key Aspect | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 💡 LED Lighting | Optimizes crop growth with energy-efficient, customizable light spectrums. |
| 💧 Hydroponics | Water-efficient cultivation method, delivering nutrients directly to plant roots. |
| 🤖 AI Automation | Enhances efficiency through environmental control and robotic planting/harvesting. |
| 📊 Data Analytics | Improves crop yields by analyzing growth patterns and environmental factors. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
Vertical farming is the practice of growing crops in vertically stacked layers inside controlled environments. This technique maximizes space and resource utilization, particularly in urban settings, to ensure year-round crop production.
▼
LED lighting is crucial because it provides energy-efficient, customizable light spectrums tailored for optimal plant growth. This leads to lower energy costs and improved crop yields in controlled environments.
▼
Hydroponics conserves water by delivering nutrients directly to plant roots without soil. This reduces water consumption by up to 90% compared to traditional farming, making it a sustainable cultivation method.
▼
AI enhances operational efficiency through environmental control, automated planting, and harvesting. It monitors conditions, optimizes resource use, and reduces labor costs, improving overall productivity.
▼
The economic benefits include reduced transportation costs, lower labor costs, and increased crop yields. Local production reduces transportation, automation cuts labor expenses, and optimized conditions boost yield.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the US vertical farming market is undergoing a technological revolution, with LED lighting, hydroponics, AI, and data analytics leading the charge. These advancements not only enhance crop yields and operational efficiency but also contribute to a more sustainable and resilient food system. As these technologies continue to evolve, the US vertical farming market is poised for continued growth and innovation.





