Agroforestry practices for biodiversity: a sustainable approach

Agroforestry practices enhance biodiversity, improve soil health, and increase crop yields by integrating trees and shrubs with agricultural systems, contributing to a more sustainable farming approach.
Agroforestry practices for biodiversity offer a harmonious approach to farming that benefits both the environment and agricultural productivity. Have you ever wondered how these methods can restore ecosystems while enhancing crop yields? Let’s dive into their significance.
Understanding agroforestry practices
Understanding agroforestry practices is crucial for anyone interested in sustainable agriculture. These practices combine agriculture and forestry to create more productive and sustainable land-use systems. By integrating trees and shrubs into crop and livestock systems, farmers can enhance biodiversity and improve ecosystem health.
Benefits of Agroforestry
Agroforestry offers a range of benefits for both the environment and farmers. It provides numerous ecological advantages, such as soil protection and improved water retention. Additionally, farmers can benefit economically through increased crop yields and diversified income sources.
- Enhances soil fertility
- Reduces soil erosion
- Improves microclimates
- Provides habitat for wildlife
Moreover, agroforestry can play a significant role in climate change mitigation. By storing carbon in trees, these practices contribute to lower greenhouse gas levels in the atmosphere. They not only offer solutions for food production but also help in combating the effects of climate variability.
Types of Agroforestry Practices
There are various types of agroforestry practices tailored to different environmental and agricultural contexts. These practices include alley cropping, silvopasture, and forest farming. Each type offers unique benefits and can be adapted based on specific land conditions and farmers’ needs.
For instance, alley cropping involves planting crops between rows of trees, which can optimize land use and reduce weeds. Silvopasture combines trees, livestock, and forage into a single system, providing shade and forage for animals while enhancing biodiversity.
As the world faces growing challenges in food security and environmental degradation, understanding agroforestry practices can guide us toward sustainable solutions. By embracing these methods, farmers can contribute to a more resilient future while enhancing their own productivity.
The impact of agroforestry on biodiversity

The impact of agroforestry on biodiversity is profound and multifaceted. By integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes, we can create habitats that support a wide range of species. This approach not only promotes the survival of various organisms but also enhances the overall resilience of ecosystems.
Enhancing Habitat Diversity
Agroforestry systems provide diverse habitats for wildlife. They create microclimates that can sustain different plant and animal species. The mixture of trees and crops fosters a more varied environment, which is essential for promoting biodiversity.
- Supports pollinators like bees and butterflies
- Provides shelter and food for birds
- Encourages beneficial insects
- Helps in maintaining healthy soil organisms
In addition to supporting wildlife, agroforestry practices can also improve the genetic diversity of crops. When farmers use diverse species and varieties, they can better adapt to environmental changes and reduce vulnerability to pests and diseases.
Soil Health and Ecosystem Benefits
The integration of trees into farming systems also benefits soil health. Tree roots stabilize the soil and reduce erosion, while their leaves and organic matter enrich the soil. This improves water retention and enhances fertility, creating a healthier environment for crops.
Furthermore, agroforestry contributes to the stability of ecosystems by helping to regulate water cycles. Trees play a critical role in maintaining hydrology, which affects not only plants but also the animals that rely on those plants. This interconnectedness illustrates the vital role of agroforestry in sustaining biodiversity.
As we continue to face challenges such as climate change and habitat loss, understanding the positive impact of agroforestry on biodiversity becomes increasingly important. These practices can serve as a model for sustainable land management, balancing agricultural productivity with ecological health.
Implementing agroforestry techniques
Implementing agroforestry techniques is a powerful way to enhance agriculture while benefiting the environment. These methods combine food production with tree planting, which can lead to healthier ecosystems. Understanding how to effectively integrate these practices can make a significant difference in both productivity and sustainability.
Getting Started with Agroforestry
When beginning to implement agroforestry techniques, it’s essential to assess the land. Start by evaluating the soil type, climate, and current crops. This assessment will help to determine which trees and crops will work best together. Planting native species is often beneficial, as they adapt well and support local biodiversity.
- Choose the right tree species for your region
- Plan planting layouts according to available space
- Consider companion planting for mutual benefits
- Incorporate elements like hedgerows and windbreaks
Another vital aspect is ensuring proper spacing between trees and crops. Adequate space allows crops to receive sufficient sunlight and nutrients. Managing this harmony between trees and crops is crucial for achieving the benefits of agroforestry.
Maintenance and Care
Once agroforestry systems are established, regular maintenance is key to their success. This includes monitoring the health of both trees and crops, managing pests, and adapting to any changes in weather patterns. Pruning trees can enhance growth and ensure that crops thrive below them.
In addition, using organic mulch around the base of trees can help retain moisture, suppress weeds, and improve soil quality. This natural method nourishes the land while enhancing the overall agroecosystem.
As farmers and landowners adopt agroforestry techniques, they not only improve their land’s productivity but also contribute to environmental preservation. This approach can lead to a more sustainable future where agricultural practices coexist with ecological health.
Case studies of successful agroforestry systems
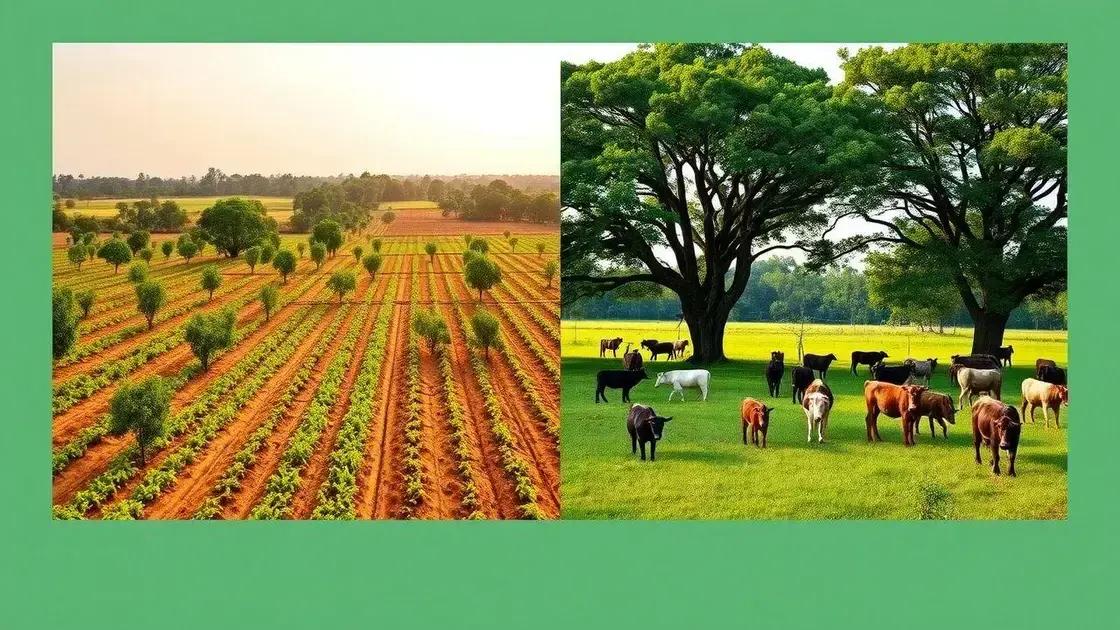

Case studies of successful agroforestry systems provide valuable insights into how these practices can positively impact farming and the environment. By examining real-world examples, we can understand the benefits and challenges of agroforestry across different regions and contexts.
Successful Example: The Alley Cropping Method
In several regions, particularly in Africa, farmers have adopted alley cropping as a practical agroforestry technique. This involves planting rows of trees alongside crops, improving yields while enhancing soil health. For instance, in Nigeria, farmers have integrated leguminous trees, which help fix nitrogen in the soil, with cereal crops. This has resulted in healthier soils and increased food production.
- Increased crop yields by 20-50%
- Enhanced soil fertility through nitrogen fixation
- Reduced soil erosion during heavy rains
- Improved resilience to drought conditions
Such practices illustrate how combining trees with crops can create a more productive and sustainable agricultural system.
A Success Story: Silvopasture
Another compelling case is found in the United States, where silvopasture has been successfully implemented. This system combines livestock grazing with tree planting, resulting in a sustainable environment for both animals and plants. Farmers in North Carolina have reported significant benefits, including improved animal health and enhanced biodiversity.
By providing shade and forage, trees contribute to better weight gain in livestock. This approach not only maintains pasture productivity but also creates habitats for wildlife, promoting a balanced ecosystem.
Moreover, the shade from trees helps to keep the soil temperature down, ensuring moisture retention and preventing heat stress in animals. Such systems demonstrate the versatility and adaptability of agroforestry techniques in different agricultural settings.
As we learn from these successful case studies, implementing agroforestry systems can lead to both environmental sustainability and improved economic outcomes for farmers. These examples showcase the potential of combining traditional farming practices with innovative techniques to achieve lasting agricultural resilience.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Agroforestry Practices
What are agroforestry practices?
Agroforestry practices involve integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural land to improve productivity, biodiversity, and sustainability.
How do agroforestry techniques benefit the environment?
These techniques enhance soil health, increase biodiversity, and help with climate change mitigation by sequestering carbon.
Can agroforestry improve crop yields?
Yes, by using trees to create a diverse ecosystem, farmers can achieve higher crop yields and enhance resilience against pests and diseases.
What are some examples of agroforestry systems?
Examples include alley cropping, silvopasture, and forest farming, each tailored to specific environmental and agricultural contexts.